Automatic Control Linear Systems PART VII
Should be the last one
Table of Contents
Lec 8 Linear feedback controllers, s.s. observers
I. Lyapunov method
a. Properties
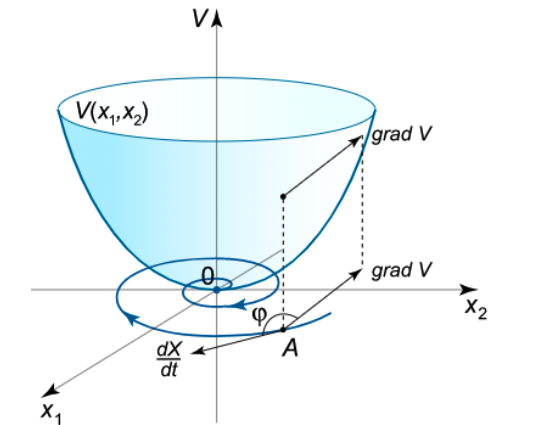
Let us consider Lyapunov functions for investigation stability of linear systems. Lyapunov functions have the next properties:
- Lyapunov function V (𝑥) must be positive definite: for any 𝑥 ∈ 𝑅𝑛
- Lyapunov function V (𝑥) is positive definite and V (𝑥) = 0 in case 𝑥 is null-vector (zero).
- Lyapunov functions must increases (decreases) uniformly with uniform increasing (decreasing) of 𝑥-vector norm.
That is, $\lim_{x\to 0}V(x)=0$ and $\lim_{x\to \infty}V(x)=\infty$
b. Lyapunov Theorem
The equilibrium 𝑥 = 0 is asymptotic stable if exists Lyapunov function V (𝑥) such that for any motion trajectories 𝑥(𝑡) starting from the arbitrary initial conditions for any time ∀𝑡 ≥ 0 the derivative of the function is negative: $\frac{dV(x(t))}{dt} < 0$.
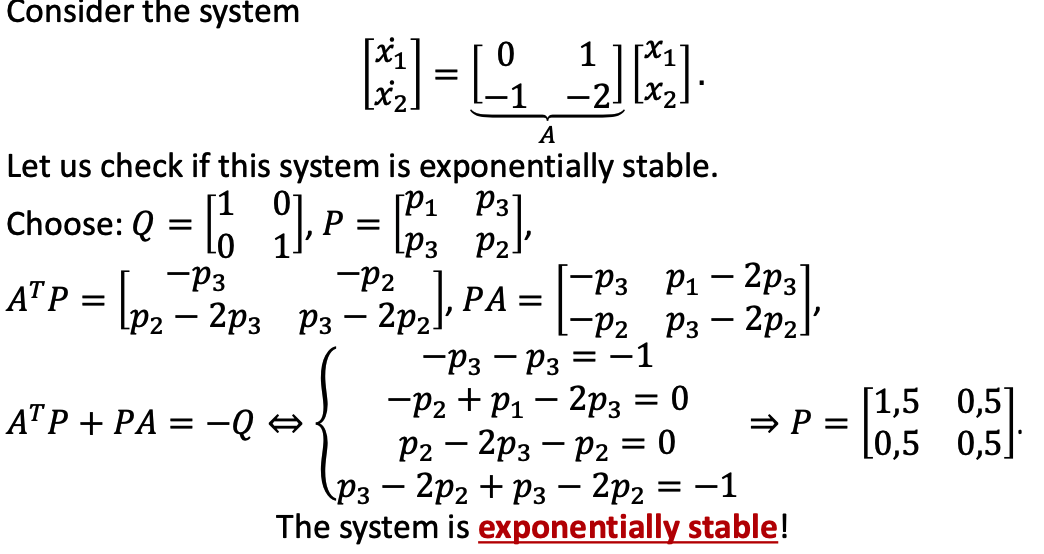
c. Example
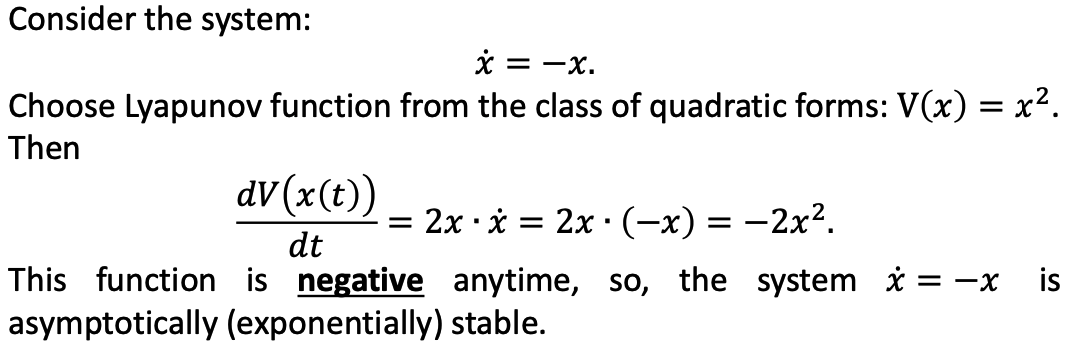
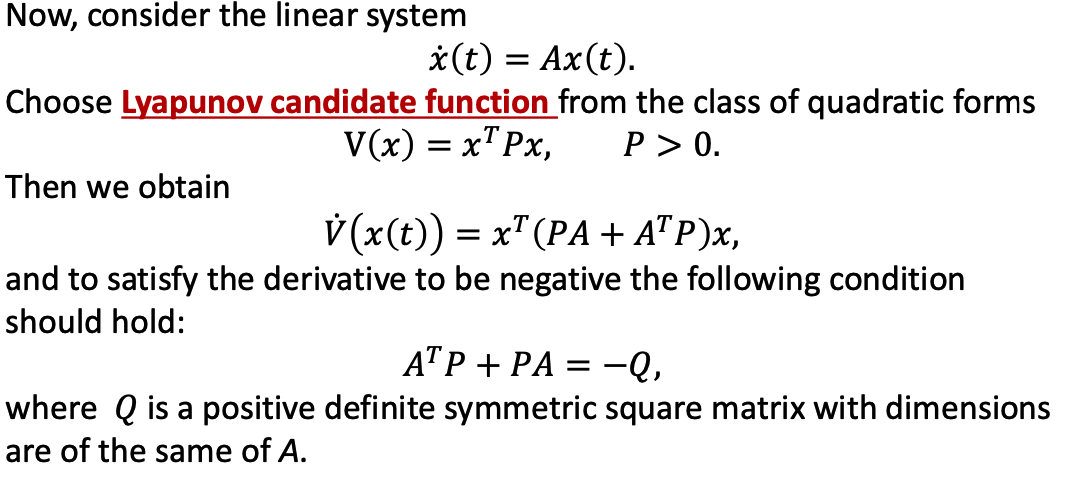
- P is symmetrical positive definite matrix. Its dimension is the same with A.
- In linear algebra, a symmetric nxn real matrix) Mis said to be positive-definite
II. State Feedback design
a. Scenary
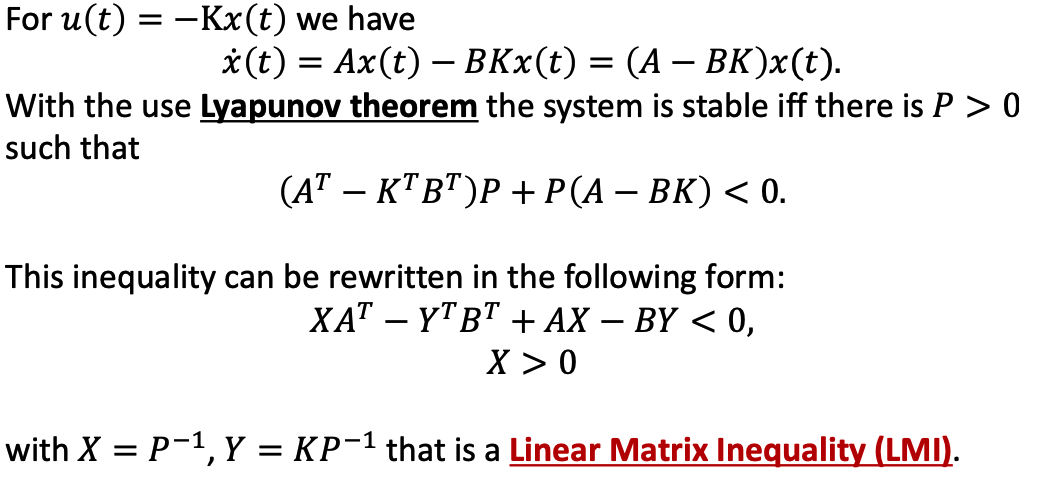
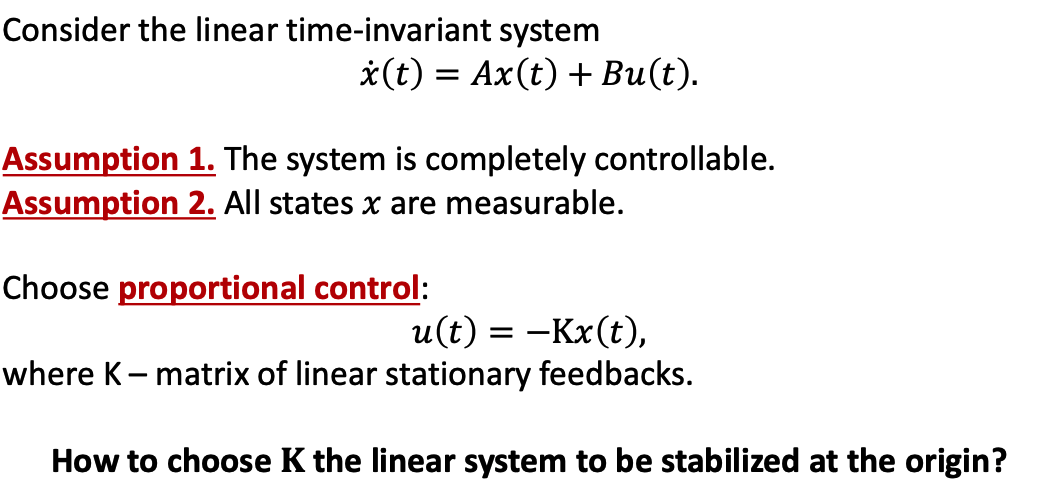
- note that the original inequality doesn’t have LMI.
b. Example
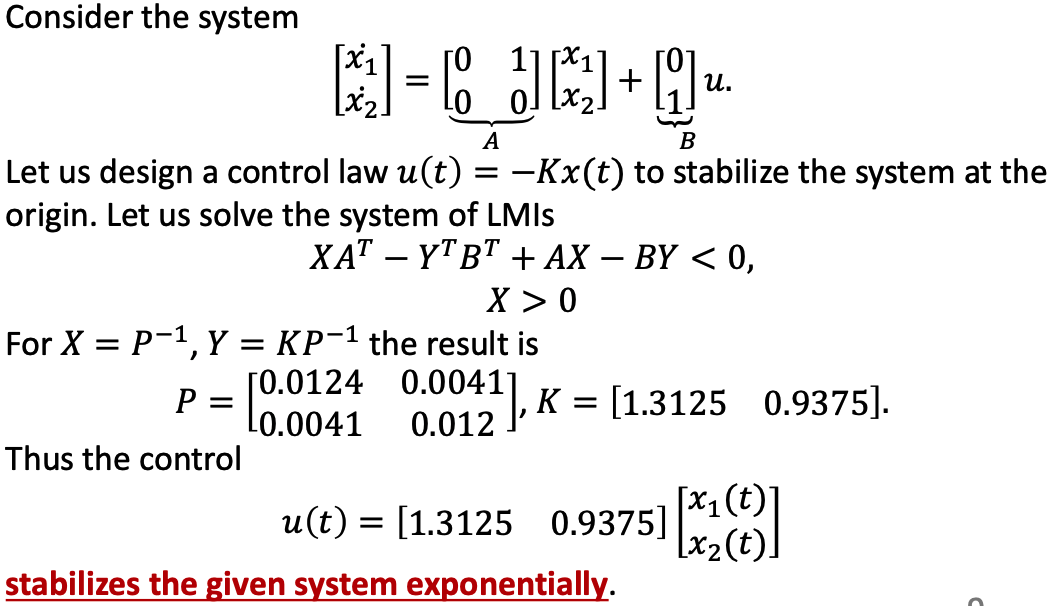
- In u(t) there should be a minus sign.
c. MATLAB realization

d. Modal Control
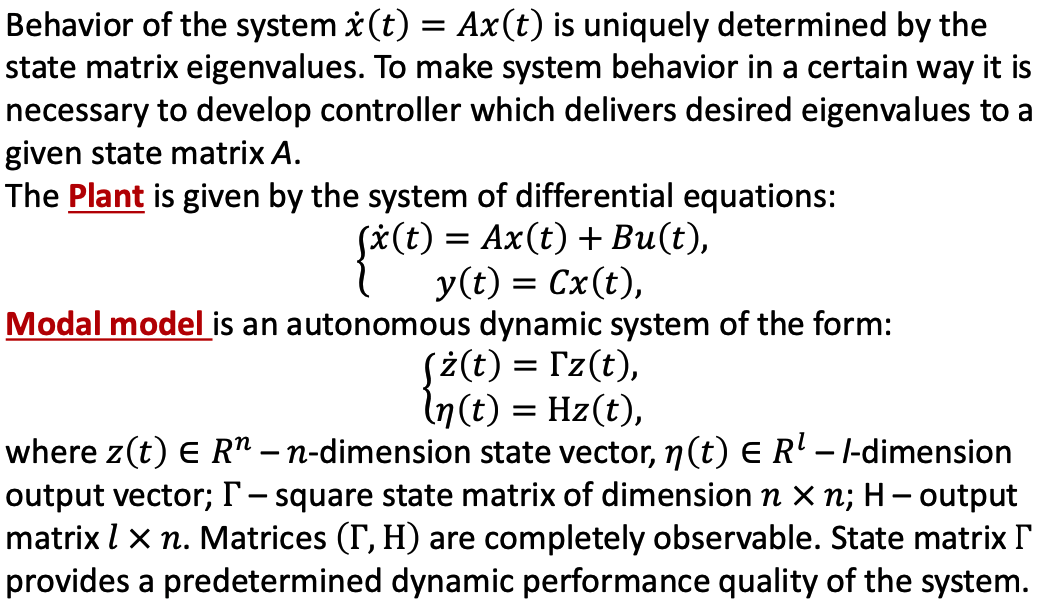
- ita and gamma in capital.
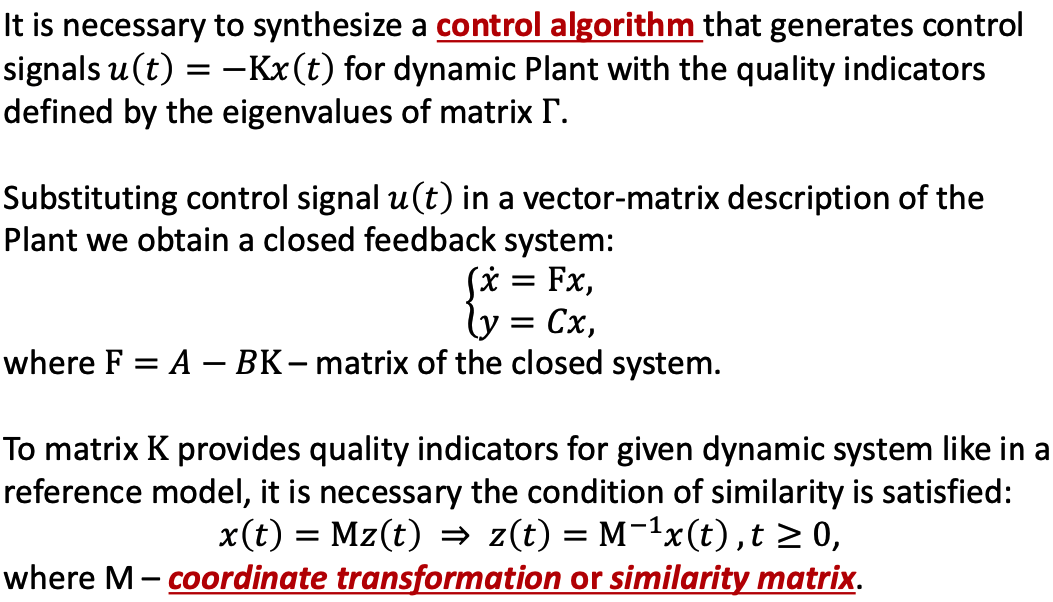
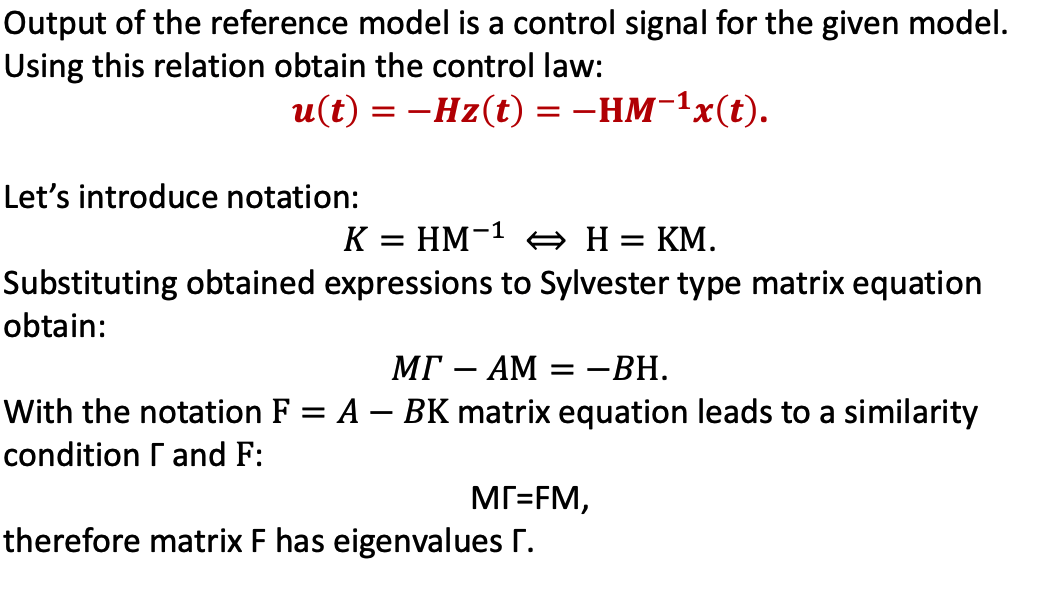
e. Example
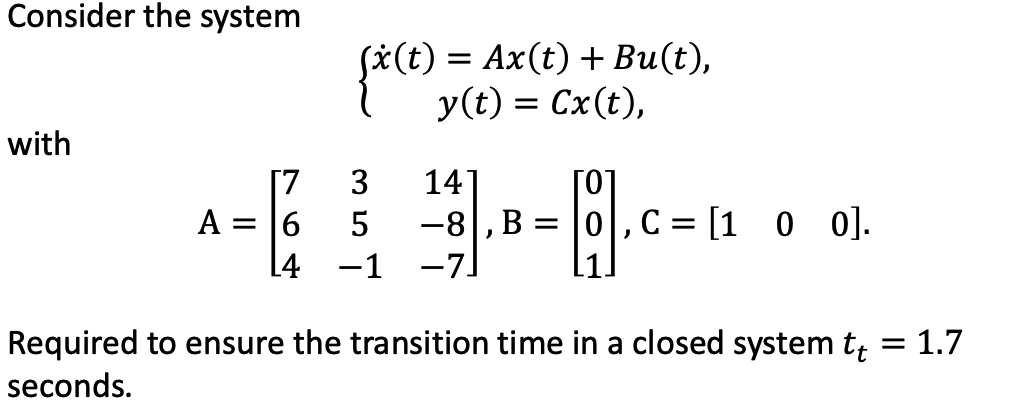
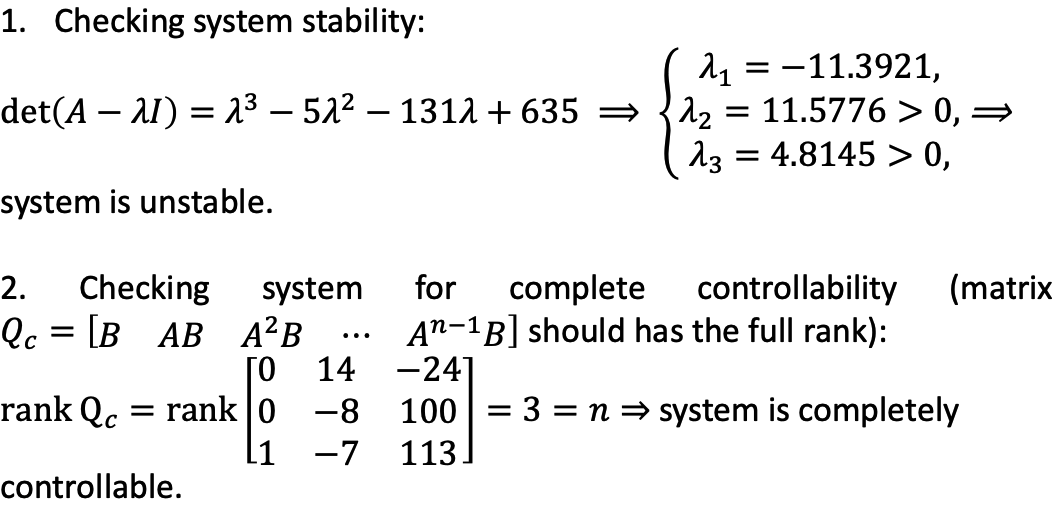
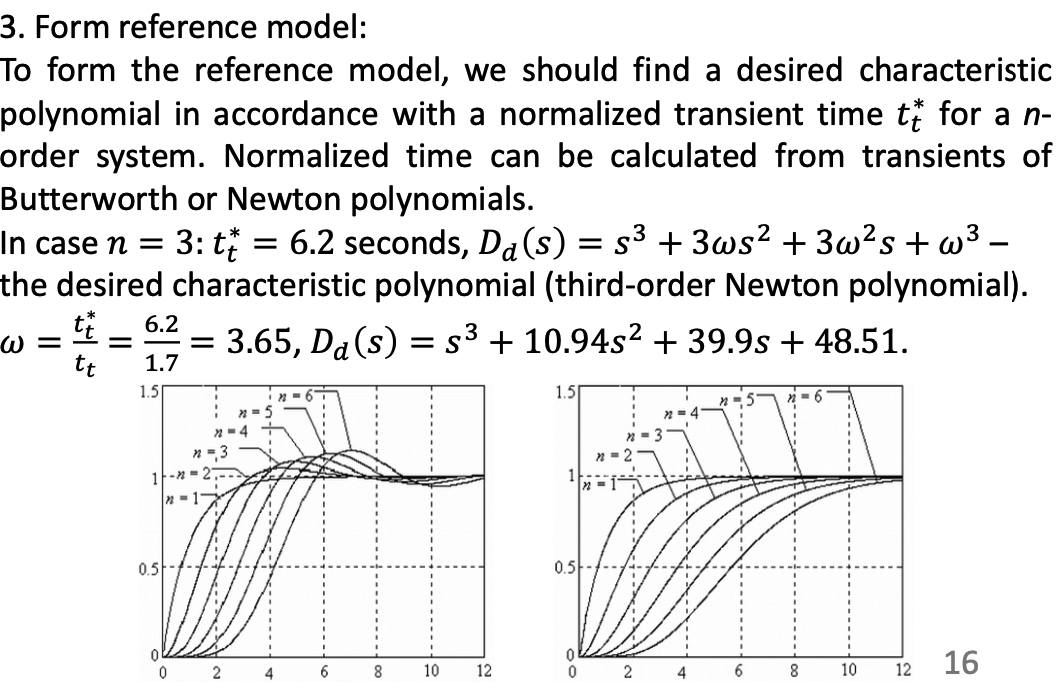
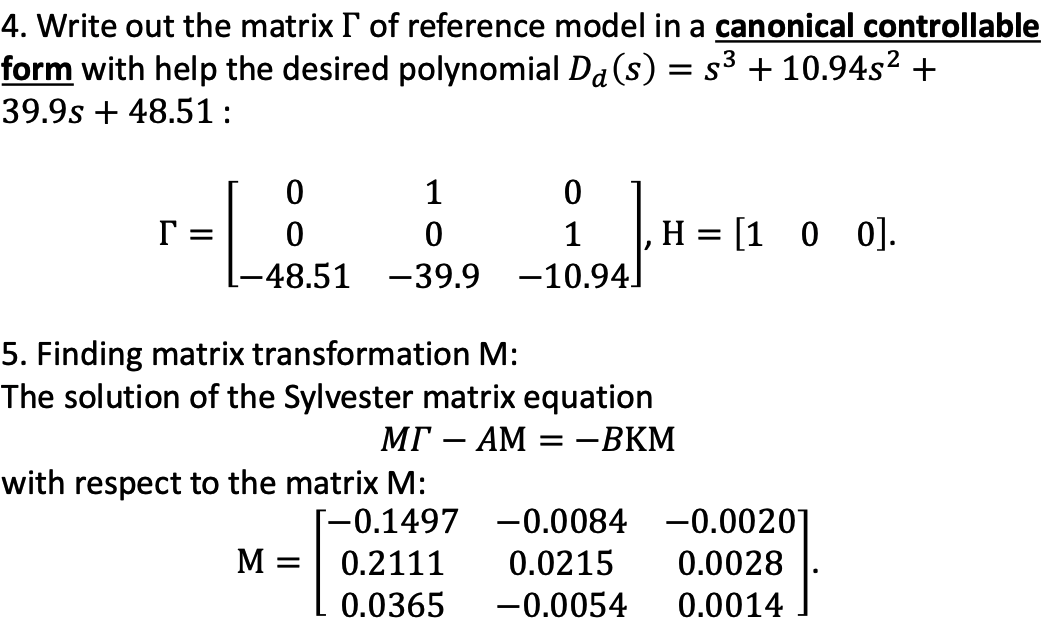
- -BKM=-BH
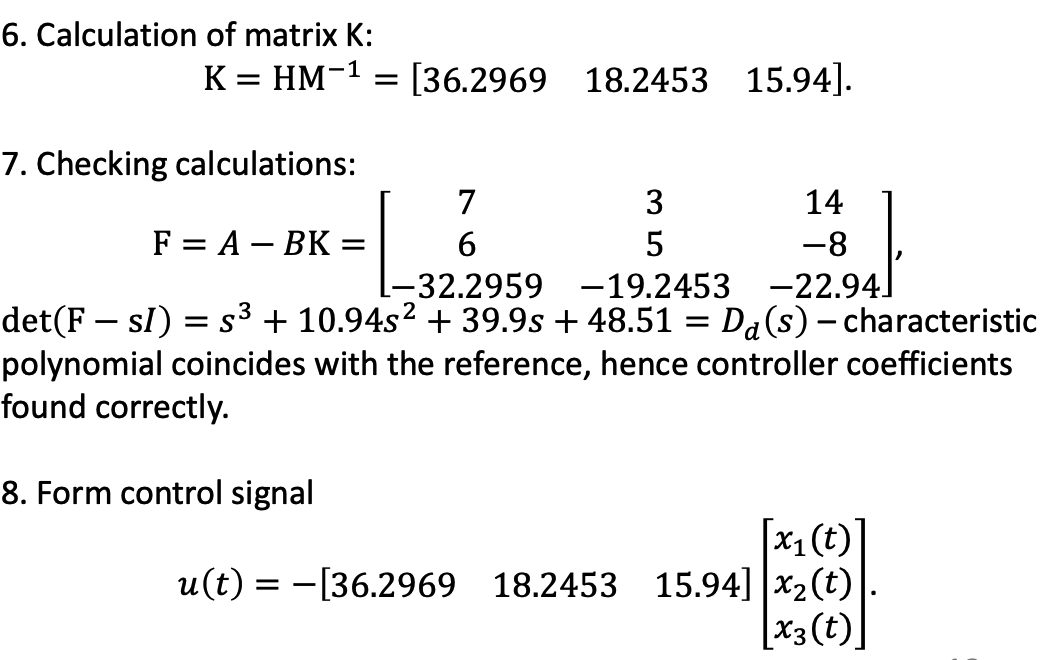
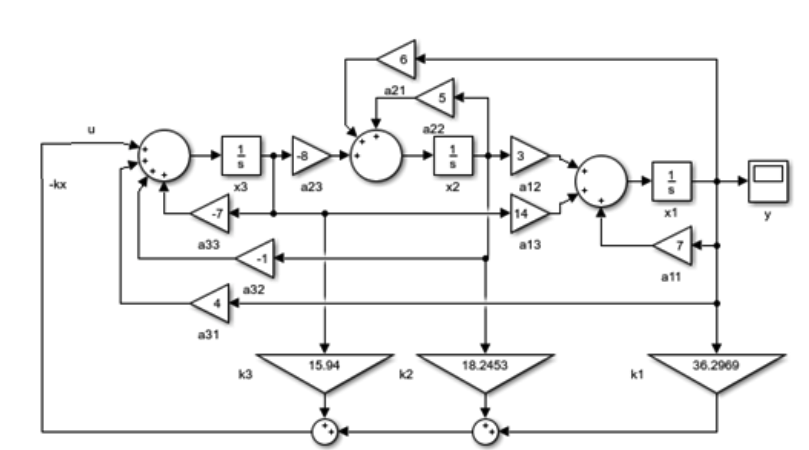
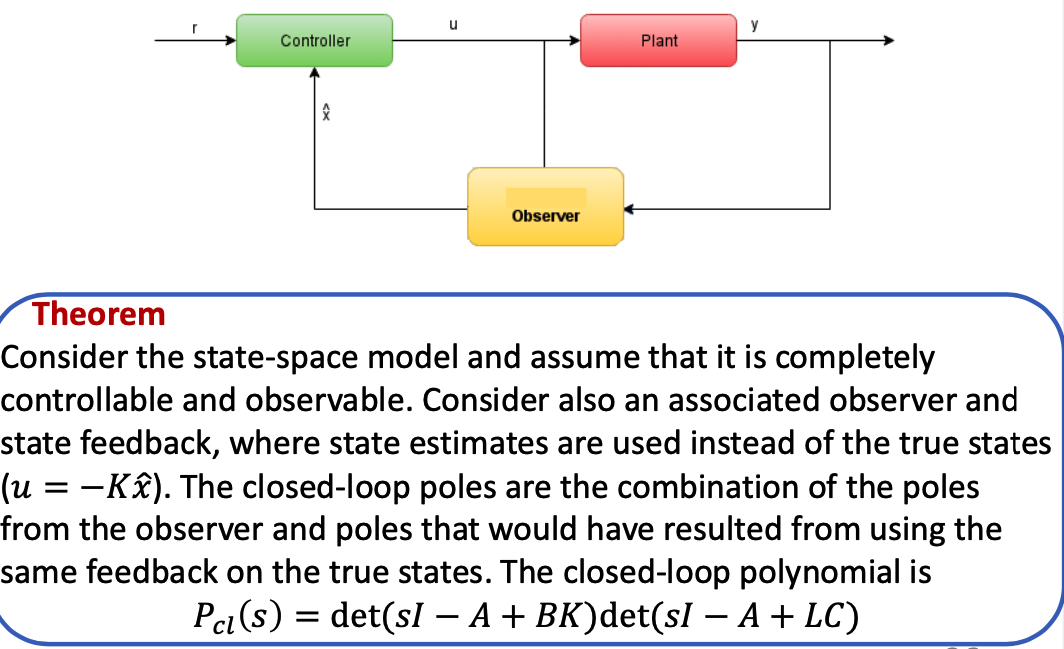
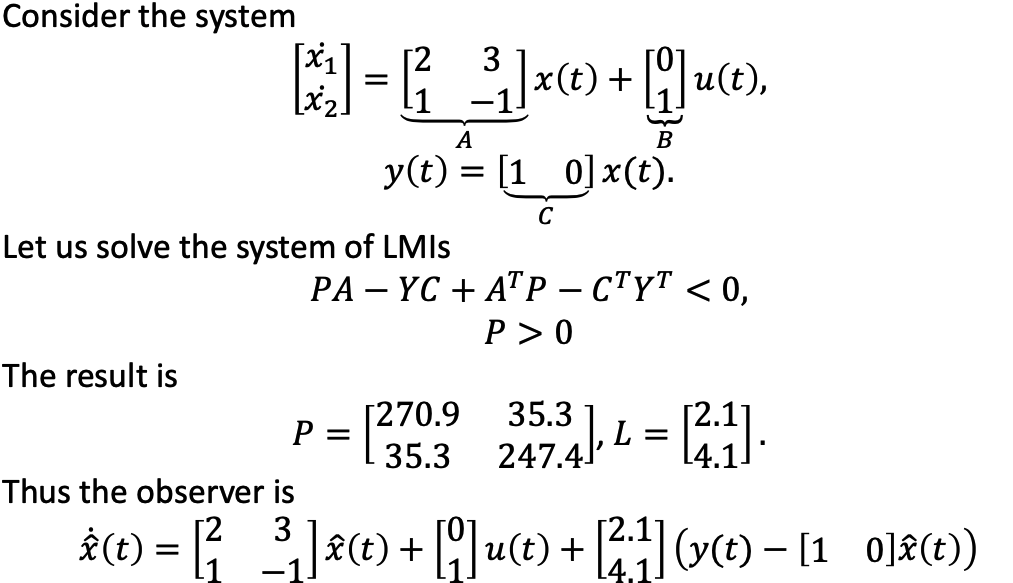
f. Observer Design
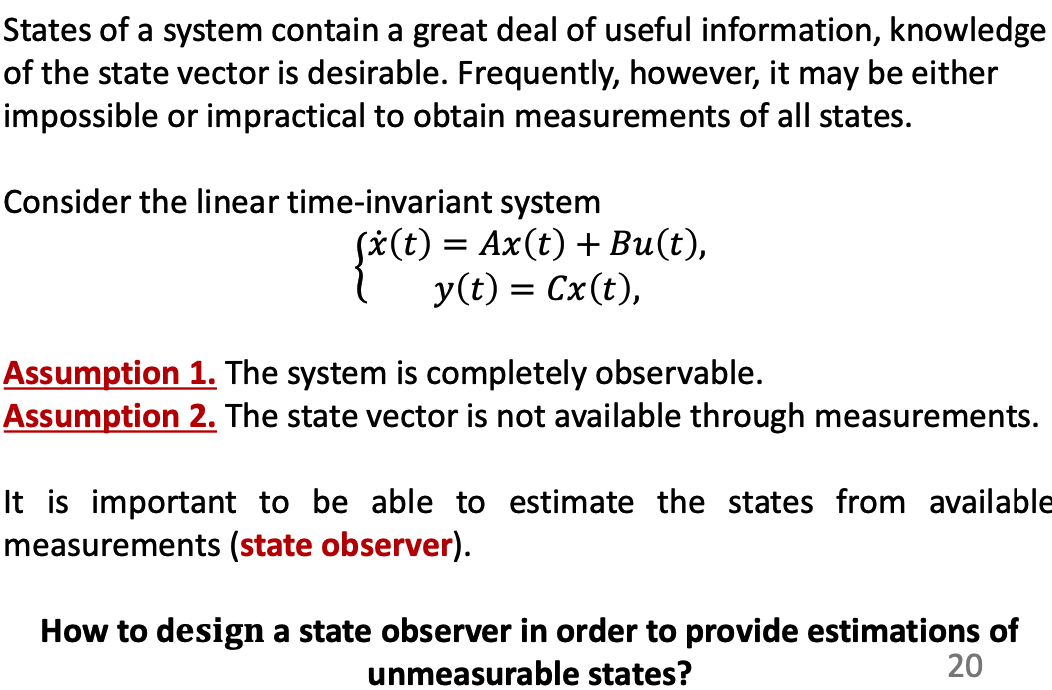
- In former lectures, we assumed that we obtain all states from output, but in practice, all states requries more moeny for sensors.
- Observer helps to see state that can’t be obtained directly.
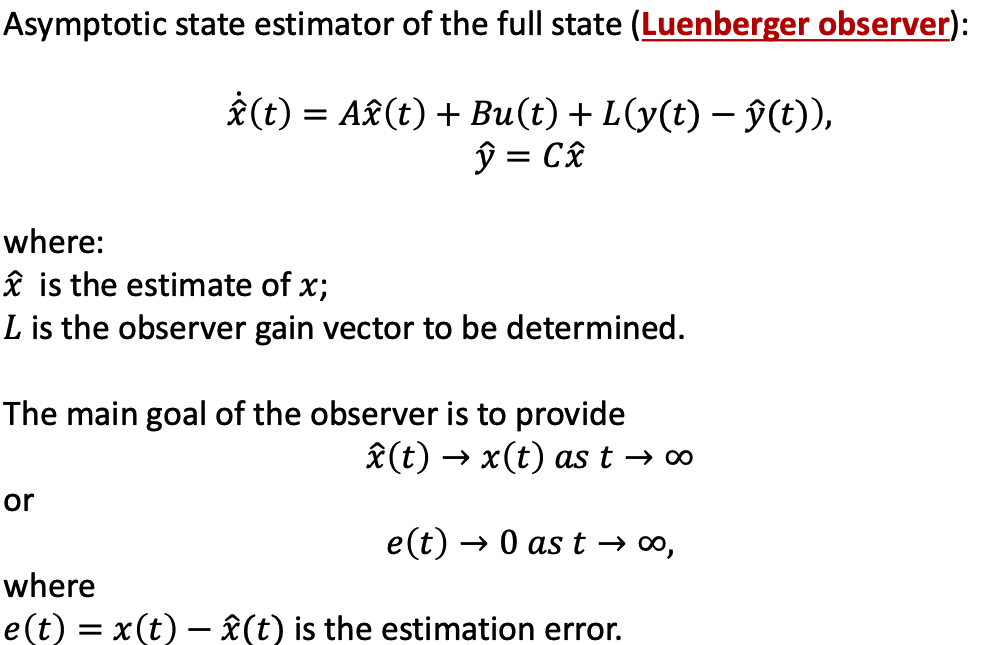
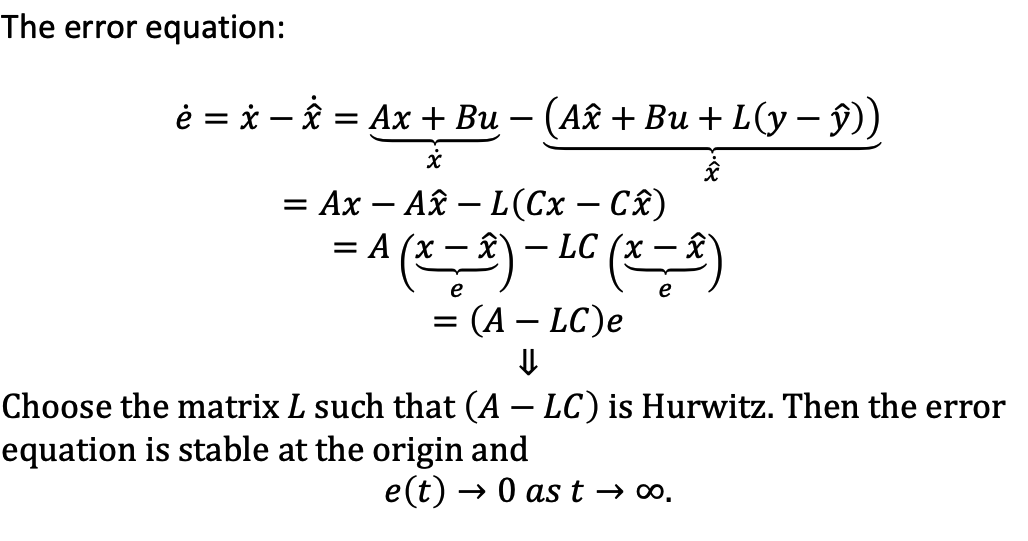

g. Example
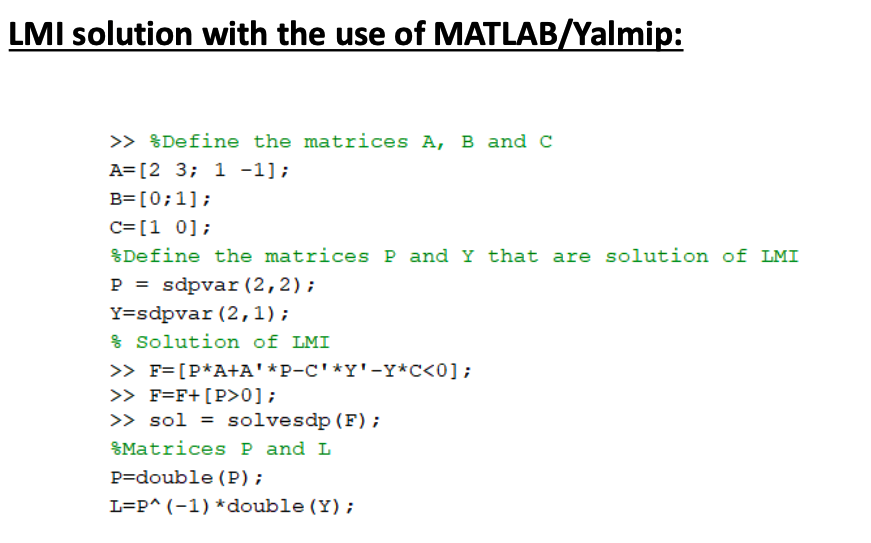
h. MATLAB realization
III. Combinition